Buffers
Sometimes it is desirable to have a solution with a pH that does not change easily. It this case, a buffer is used.
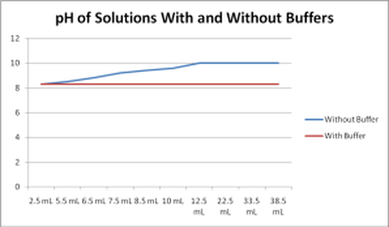
A buffer is a liquid solution which resists change in pH. When reasonable quantities of weak acid, weak base, strong acid or strong base are added to the solution, its pH remains the same.
A buffer is created by combing a weak acid with its conjugate base, or by combing a weak base with its conjugate acid.
A buffer is a liquid solution which resists change in pH. When reasonable quantities of weak acid, weak base, strong acid or strong base are added to the solution, its pH remains the same.
A buffer is created by combing a weak acid with its conjugate base, or by combing a weak base with its conjugate acid.
Explanation:
A buffer works because it is able to neutralize reasonable quantities of acids or bases that are added to the solution.
A buffer works because it is able to neutralize reasonable quantities of acids or bases that are added to the solution.
- When hydrogen ions are added into the solution, the base or conjugate base (depending on the solution) will neutralize them.
- When hydroxide ions are added into the solution, the acid or conjugate acid (depending on the solution) will neutralize them.
Real Life Uses
There are commercial applications for buffers. Shampoo is required to be a buffer, so that an acidic or basic product does not accidentally burn your scalp. The same is true for many other types of manufactured soaps.
The human body has has its own buffers. This is necessary so that when a person a person
consumes something acidic or basic, he or she does not automatically die.
consumes something acidic or basic, he or she does not automatically die.
The process of dying fabrics requires a constant pH, and therefor, a buffer solution.
Finished with Buffers?
Test your knowledge of neutralization
Test your knowledge of neutralization